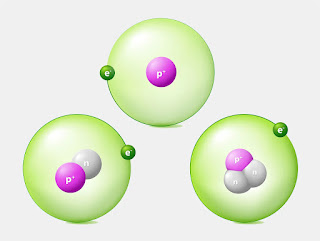
Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus, but a different number of neutrons. This means that isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number, but a different atomic mass. Isotopes are commonly referred to by their atomic mass, with the suffix -ium added to the end of the name of the element. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
One of the most interesting facts about isotopes is that they are not just found in laboratory settings, but are also present in nature. In fact, almost all elements have at least one naturally occurring isotope. Some elements, like uranium, have several isotopes that occur naturally. Another interesting fact about isotopes is that they can be stable or unstable. Stable isotopes are those that do not undergo radioactive decay, while unstable isotopes are those that do undergo radioactive decay. Unstable isotopes will eventually decay into other elements, releasing radiation in the process.
Isotopes can be useful in a variety of applications, including medicine and industry. In medicine, isotopes are used in imaging technologies like PET scans, which can help doctors diagnose diseases. In industry, isotopes are used in a process called isotope labeling, which involves replacing a small number of atoms in a molecule with isotopes of the same element. This allows scientists to track the movement of atoms within a molecule, which can provide valuable information about the molecule’s behavior.
In addition to their practical applications, isotopes can also provide valuable information about the origins and history of the universe. Because isotopes can be created through natural processes, like the fusion of elements in stars, the relative abundance of different isotopes in a sample can reveal information about the conditions under which the sample was formed. For example, the ratio of carbon-12 to carbon-14 in a sample can provide information about the age of the sample and the conditions under which it was formed.
Isotopes are also important in the study of climate change. Some isotopes, like carbon-14 and oxygen-18, are particularly sensitive to changes in temperature and can provide valuable information about past climates. By analyzing the isotope composition of samples from different periods in Earth’s history, scientists can learn more about how the climate has changed over time and how it is likely to change in the future.
Isotopes can also be artificially created in a laboratory through a process called isotope enrichment. This involves separating isotopes of an element from each other based on their relative atomic mass. Isotope enrichment can be useful for creating isotopes that have specific applications, such as isotopes used in medical imaging or isotopes used in isotope labeling. Isotope enrichment can be achieved through a variety of methods, including centrifugation, gaseous diffusion, and laser-induced fluorescence.
Isotopes are an important and fascinating aspect of chemistry and the study of the universe. From their practical applications in medicine and industry, to their role in the study of the origins and history of the universe, isotopes continue to provide valuable insights and information.