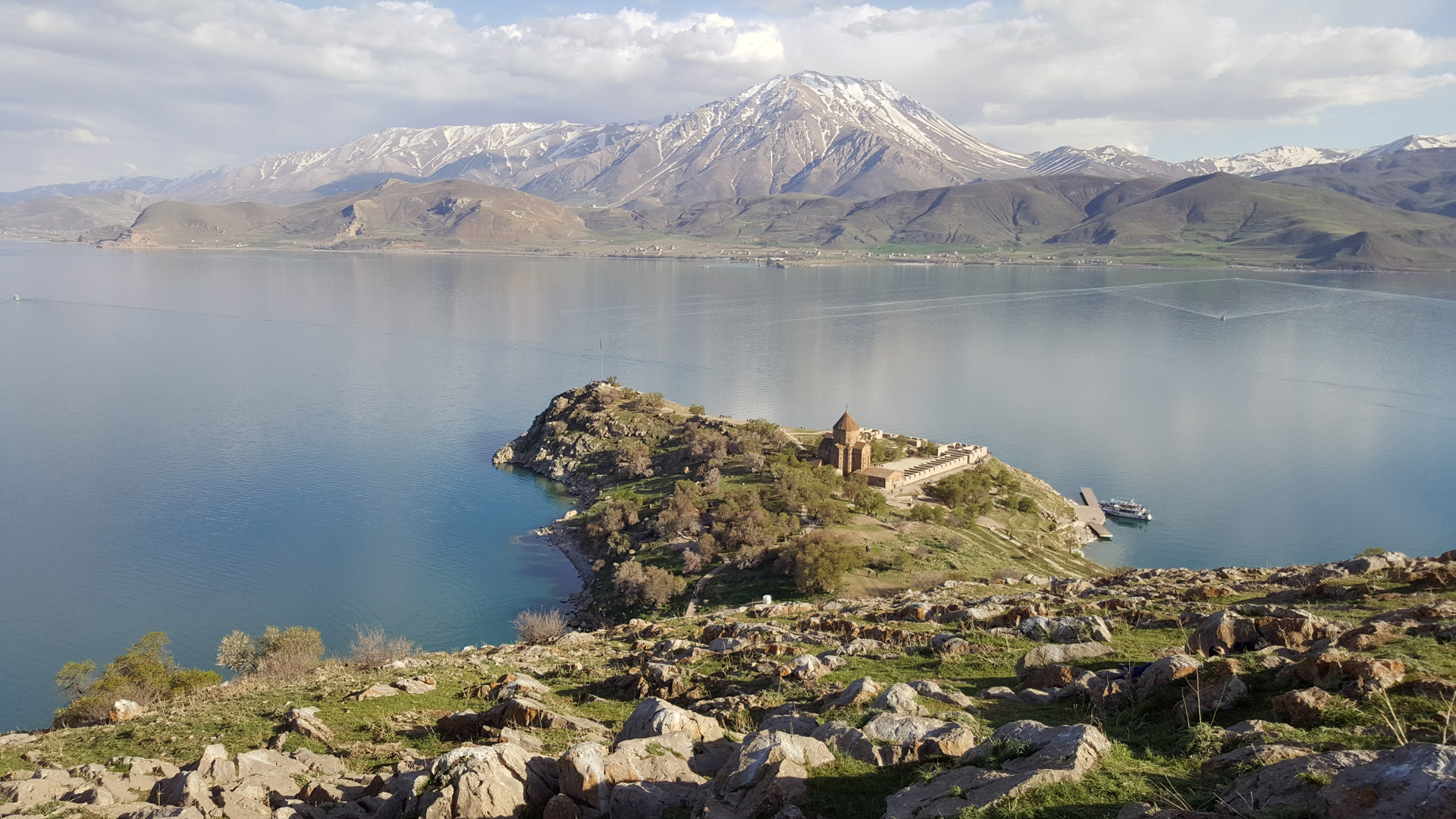
Nestled in the heart of Eastern Anatolia, Turkey, Lake Van stands as a captivating natural wonder with a history as deep as its waters. Stretching over 3,755 square kilometers, it reigns as the largest lake in the country, embraced by the picturesque landscape of the Armenian Highlands. From its geological origins over three million years ago to its pivotal role in ancient civilizations, Lake Van has borne witness to a tapestry of events that have shaped the region’s cultural, historical, and environmental heritage. Join us as we embark on a journey to explore 25 interesting facts and numerical trivia that unveil the essence of this ancient and majestic lake.
Formation: Lake Van, a geological marvel, emerged over three million years ago through a complex interplay of tectonic and volcanic processes shaping the Armenian Highlands. This ancient basin’s formation is a testament to the dynamic geological history of the region, providing a unique ecosystem that has endured for millennia.
Size: Towering as the largest lake in Turkey, Lake Van sprawls over 3,755 square kilometers, a vast expanse that captivates with its scenic grandeur. Its sheer size not only makes it a prominent geographic feature but also underscores its ecological importance within the Anatolian landscape.
Depth: Plummeting to depths of about 450 meters, Lake Van ranks among the deepest lakes globally. Its profound depths contribute to its distinctive ecosystem, harboring a variety of aquatic life adapted to the lake’s varying thermal and saline stratification.
Altitude: Perched at an elevation of 1,640 meters above sea level, Lake Van sits majestically in the mountainous terrain of Eastern Anatolia. The high altitude not only contributes to the lake’s breathtaking surroundings but also influences its climate and water dynamics.
Endorheic Nature: Lake Van’s endorheic character, with no outflow to the sea, encapsulates its self-contained hydrological system. The absence of a natural outlet underscores the lake’s reliance on precipitation and inflowing rivers, creating a delicate balance in the water cycle.
Salinity: The lake’s moderate salinity levels, varying with depth and location, shape the composition of its waters. This salinity, coupled with other environmental factors, influences the types of organisms that thrive in Lake Van, contributing to its unique biodiversity.
Islands: Among its scenic archipelago, Akdamar Island stands out as the largest. Home to the iconic Akdamar Church, this island carries historical and cultural significance, serving as a tangible link to the region’s past civilizations.
Historical Significance: Lake Van’s shores bear witness to a rich tapestry of human history, with evidence of ancient civilizations dating back to the Urartian period. The lake’s environs have hosted vibrant cultures, leaving behind archaeological treasures that illuminate the region’s historical importance.
Urartian Kingdom: Flourishing between the 9th and 6th centuries BCE, the Urartian civilization left an indelible mark on Lake Van’s landscape. The remnants of Urartian settlements and inscriptions tell a compelling story of an advanced society that once thrived in this high-altitude region.
Van Castle: Perched dramatically on the shores of Lake Van, the Van Castle, initially constructed by the Urartians and later expanded by subsequent civilizations, stands as a testament to the strategic importance of the region. The castle’s imposing walls and towers offer a glimpse into the military and architectural prowess of its builders, providing a tangible link to the region’s historical defense strategies.
Armenian Kingdom: Nestled within the embrace of Lake Van, the region played a pivotal role in the ancient Armenian Kingdom. Its shores witnessed the ebb and flow of Armenian influence, and the cultural imprints of this kingdom endure in the historical landmarks scattered around the lake, connecting the present to a rich and storied past.
Historical Battles: Lake Van’s surroundings bore witness to the epochal Battle of Manzikert in 1071, a turning point in history where the Byzantine Empire clashed with the Seljuk Turks. The outcomes of this battle rippled across the region, shaping the geopolitical landscape for centuries to come.
Migration Routes: Acting as a crossroads for various cultures and civilizations, the region surrounding Lake Van has long served as a nexus for trade and migration routes. The convergence of diverse peoples in this strategic location has left an enduring legacy in the cultural tapestry of the area.
Armenian Genocide: Tragically, the serene shores of Lake Van became a witness to the horrors of the Armenian Genocide during World War I. The displacement and persecution of Armenians along the lake’s periphery stand as a poignant chapter in the region’s history, echoing the broader impact of the events of that era.
Post-World War I Changes: In the aftermath of World War I, Lake Van and its environs underwent significant territorial changes as the Republic of Turkey emerged. The redrawing of borders and the establishment of new political entities shaped the modern geopolitical configuration around the lake.
Modern Agriculture: Fertile lands hugging Lake Van have sustained agricultural activities for centuries. The cultivation of crops such as wheat, barley, and the flourishing fruit orchards not only supports local livelihoods but also enriches the region’s economic landscape.
Van Cat: Native to the region, the Van cat is a unique and resilient breed known for its striking color pattern and remarkable swimming abilities. This feline companion has become an intrinsic part of the cultural identity of those living in the vicinity of Lake Van.
Earthquakes: The seismic activity of the region has left its mark on the landscape, with historical earthquakes shaping the terrain around Lake Van. The geological dynamism underscores the ever-changing nature of the earth beneath this ancient lake.
Tourism: Lake Van, with its cultural heritage sites like the Akdamar Church and Van Castle, beckons tourists seeking to unravel the mysteries of its past. The lake’s shores offer a blend of historical exploration and natural beauty, attracting visitors from around the globe.
Biodiversity: Beneath the rippling waters of Lake Van lies a diverse aquatic ecosystem, home to various fish species. The lake’s environs also provide a habitat for numerous bird species, making it a haven for birdwatchers fascinated by the avian diversity flourishing in this unique landscape.
Hydropower: Lake Van’s potential for hydropower generation has been a subject of exploration, reflecting efforts to harness its energy resources. Proposed projects aim to tap into the lake’s hydroelectric potential, contributing to the region’s energy infrastructure.
Environmental Concerns: The ecological balance of Lake Van has faced challenges, including pollution and changes in water quality. Ongoing environmental concerns have spurred conservation efforts, emphasizing the need to protect the lake’s delicate ecosystem for future generations.
Transportation: Throughout history, Lake Van has served as a vital transportation route, facilitating trade and connecting regions. Its strategic location has made it a conduit for the movement of goods and people, contributing to the economic and cultural exchanges in the surrounding areas.
Population Centers: Cities and towns dotting the shores of Lake Van, such as the city of Van, have evolved into vibrant population centers. These urban hubs are not only economic and administrative focal points but also repositories of the cultural and historical heritage of the region.
Scientific Studies: Lake Van has become a focal point for scientific inquiry, with researchers delving into various disciplines. Geological, ecological, and archaeological studies have advanced our understanding of the lake’s history, environment, and the intricate interactions shaping this unique geographic locale. The ongoing scientific exploration of Lake Van continues to contribute valuable insights to broader fields of study.