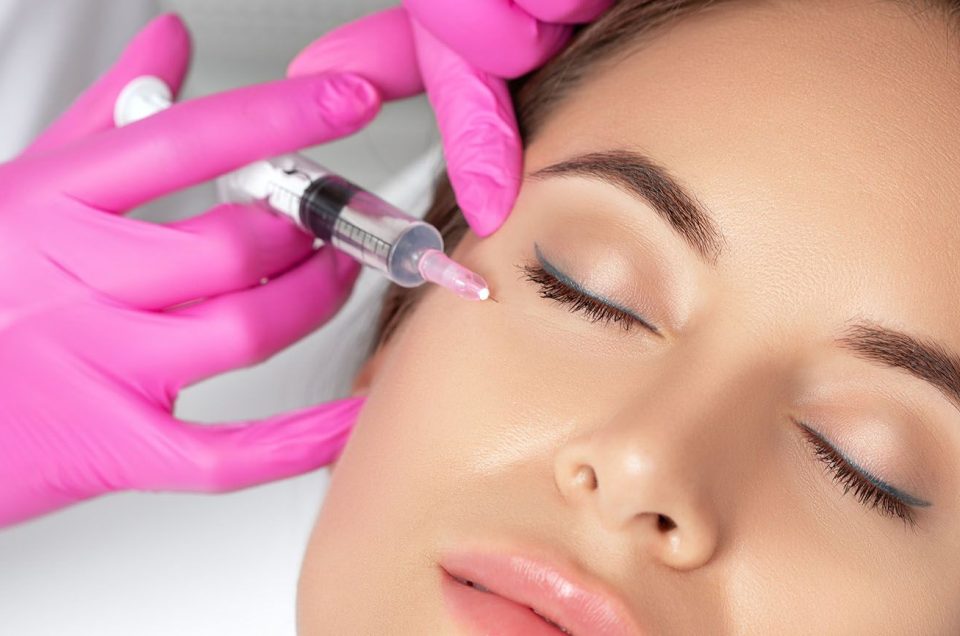
Botox, which is short for Botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein that is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. This potent toxin was first discovered in 1895 by Emile Pierre van Ermengem, a Belgian microbiologist. Botulinum toxin is known to cause a serious type of food poisoning called botulism, which can lead to paralysis and even death. However, in smaller doses, this toxin has been found to have therapeutic benefits.
In 1978, Dr. Alan Scott made a groundbreaking discovery when he used botulinum toxin to treat strabismus, also known as crossed eyes. This marked the first documented use of botulinum toxin as a medical treatment. Dr. Scott found that injecting small amounts of the toxin into the affected eye muscles could temporarily paralyze them, allowing the eyes to align properly.
In 1989, the FDA approved the use of Botox for treating eye muscle disorders such as blepharospasm and strabismus. This approval allowed Botox to be used as a safe and effective treatment for people with these conditions.
In 2002, the FDA approved the use of Botox for cosmetic purposes to treat frown lines between the eyebrows. This approval was a major milestone for the cosmetic industry, as it marked the first time that Botox was officially recognized as a cosmetic treatment. Since then, Botox has become the most popular non-surgical cosmetic treatment in the world, with millions of people seeking treatment to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The market for botulinum toxin products has been growing rapidly in recent years, with a global value of $4.7 billion in 2019. This growth is largely driven by the increasing popularity of Botox, which is currently the most commonly used botulinum toxin product worldwide. In fact, over 7 million Botox treatments were performed in 2020 alone, highlighting the significant demand for this non-surgical cosmetic treatment.
In addition to its cosmetic applications, Botox has also been approved by the FDA for various medical uses. In 2018, the FDA approved Botox for the treatment of chronic migraines, which is a type of headache that occurs on 15 or more days per month. This approval has been a major breakthrough for migraine sufferers, as Botox has been shown to significantly reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
Another medical application of Botox is in the treatment of excessive sweating, a condition known as hyperhidrosis. When injected into the affected areas, Botox works to block the release of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger that stimulates the sweat glands. This helps to reduce the amount of sweat produced and can provide relief for those with excessive sweating.
While the effects of Botox are not permanent, they are long-lasting and typically last between 3-6 months. After this time, the treatment must be repeated to maintain the results. It is important to note that the results of Botox can vary depending on the individual and the area being treated. Additionally, it is crucial to receive Botox treatments from a licensed and experienced healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Botox injections are typically administered by a licensed healthcare provider who has received specialized training in the administration of Botox. This is because the injection must be administered in a specific way to ensure that it is both safe and effective. In addition, the healthcare provider will evaluate the patient’s medical history, allergies, and any medications they may be taking to determine if Botox is a suitable treatment option for them. The healthcare provider will also discuss the potential risks and benefits of the treatment with the patient, including the possibility of side effects.
In addition to its cosmetic and medical uses, Botox is also used in research to study nerve function. Because Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger that stimulates muscle contractions, it can be used to investigate how nerves and muscles interact in various conditions. Researchers have used Botox to study a wide range of neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and cerebral palsy. These studies have provided valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of these disorders and have helped to develop new treatment strategies.
The use of Botox has also been studied as a potential treatment for depression. In 2013, a study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that Botox injections could reduce symptoms of depression by as much as 47%. The study involved 74 patients with major depression, half of whom received Botox injections in their forehead muscles, while the other half received a placebo injection. The researchers found that the group that received the Botox injections had significantly lower depression scores than the placebo group, suggesting that Botox may have therapeutic potential for treating depression.
Despite its proven effectiveness and widespread use, the safety of Botox has been questioned by some critics, who argue that it may have long-term effects on nerve function. However, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety of Botox when used properly by a licensed healthcare provider. In fact, Botox is one of the most extensively studied medical treatments available, with a long track record of safety and efficacy. The most common side effects of Botox injections are temporary and include redness, swelling, and bruising at the injection site. More serious side effects are rare but can include muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, and breathing problems. It is crucial to receive Botox treatments from a licensed and experienced healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
There have been several cases of adverse reactions to Botox injections, including muscle weakness, blurred vision, and difficulty breathing. While these reactions are rare, they can occur if the injection is administered improperly or if the patient has an underlying medical condition that makes them more susceptible to adverse effects. For this reason, it is important to receive Botox injections only from a licensed healthcare provider who has received specialized training in the administration of Botox.
Botox is not recommended for use during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, as the effects of the treatment on the developing fetus or infant are not well understood. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult with their healthcare provider before considering Botox as a treatment option.
In 2020, Allergan, the manufacturer of Botox, was acquired by AbbVie for $63 billion. This acquisition represented one of the largest pharmaceutical mergers in history and solidified AbbVie’s position as a major player in the global pharmaceutical industry. The acquisition was driven in part by the popularity of Botox as a treatment for both cosmetic and medical conditions, as well as the potential for future growth in these markets.
In addition to Botox, Allergan produces a variety of other pharmaceutical and medical products, including breast implants and dermal fillers. These products are used for a range of cosmetic and medical purposes, from enhancing the appearance of the breasts to filling in wrinkles and lines on the face. Allergan’s diverse product portfolio has helped to establish it as a leader in the aesthetics industry.
The price of Botox injections can vary depending on factors such as the location and experience of the healthcare provider. Generally, Botox treatments are priced per unit, with the average cost per unit ranging from $10 to $20. The number of units required for each treatment will depend on the area being treated and the severity of the condition. It is important to note that while cost is an important consideration, patients should prioritize the qualifications and experience of the healthcare provider when selecting a Botox provider.
Botox has become a popular cosmetic treatment in recent years, with the average cost of a single treatment in the United States ranging from $300 to $600. The cost can vary depending on the location of the healthcare provider and the extent of the treatment. However, it is worth noting that the effects of Botox typically last between 3-6 months, so patients may need to undergo multiple treatments to maintain their desired results.
According to a 2017 survey conducted by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, 64% of Botox users were women. The majority of these women were between the ages of 35 and 50, although Botox is increasingly being used by younger patients as a preventative measure to delay the onset of wrinkles.
Botox is most commonly used to treat wrinkles on the forehead, between the eyebrows, and around the eyes. It works by blocking the signals between nerves and muscles, which temporarily weakens the muscle and reduces the appearance of wrinkles. The procedure is generally painless and takes only a few minutes to complete.
However, it is important to choose a licensed healthcare provider with experience in administering Botox injections. While the procedure is generally safe, there have been cases of adverse reactions such as muscle weakness, blurred vision, and difficulty breathing. In addition, Botox is not recommended for use during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Botox has proven to be a valuable tool in the field of cosmetic and medical treatments. It has the potential to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and treat a variety of medical conditions, including chronic migraines and excessive sweating. As with any medical procedure, it is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits before undergoing treatment.