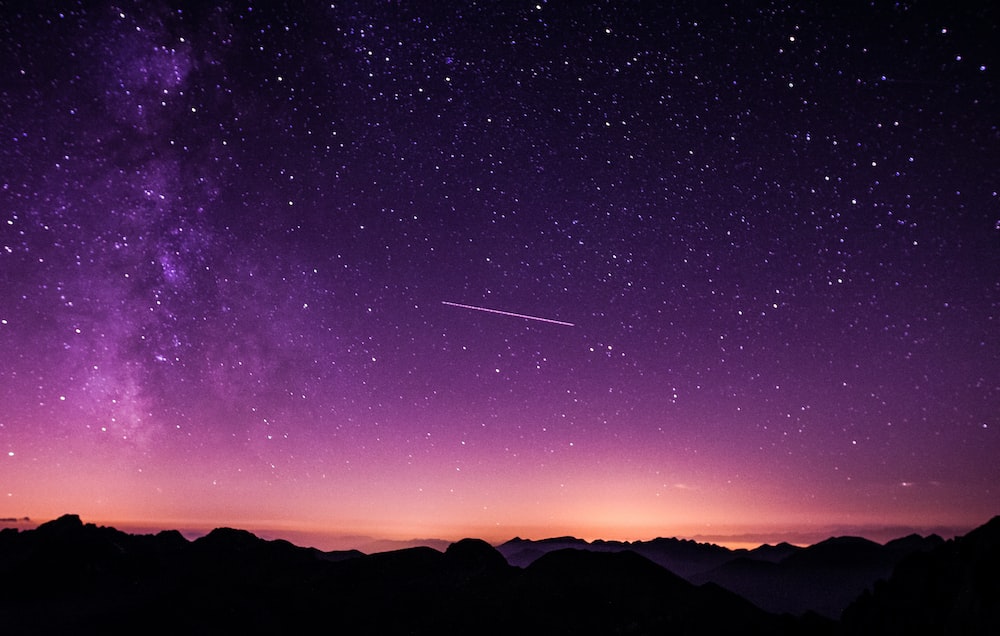
Astronomy is the study of celestial objects and phenomena such as stars, planets, galaxies, and black holes. It is one of the oldest disciplines, with origins in ancient civilizations that utilized the stars to travel and measure time. To investigate the cosmos and answer basic questions about our place in it, contemporary astronomy relies on advanced technology such as telescopes, spacecraft, and supercomputers. Astronomy continues to captivate and inspire people of all ages, from the inner workings of our own solar system to the most distant objects in the cosmos.
Here are some interesting facts about Astronomy:
The sun is actually a star, and it’s classified as a G-type main-sequence star. The sun is the closest star to Earth, and it’s responsible for providing energy to all life on our planet. As a main-sequence star, it’s in the middle of its life cycle and will eventually run out of fuel and expand into a red giant.
The Andromeda Galaxy, the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way, is approaching us at a rate of about 110 kilometers per second. Andromeda is about 2.5 million light-years away from us, but due to the expansion of the universe, it’s getting closer to us every day. In about 4.5 billion years, Andromeda and the Milky Way are expected to collide and merge into one larger galaxy.
The largest volcano in the solar system is Olympus Mons, located on Mars. Olympus Mons is about 22 kilometers high, which is more than three times the height of Mount Everest, the tallest mountain on Earth. It’s also about 600 kilometers wide, making it one of the largest volcanoes in the solar system.
The fastest spinning object known in the universe is a millisecond pulsar, which can rotate at up to 43,000 revolutions per minute. Pulsars are incredibly dense and compact objects that are created when a star explodes in a supernova. They emit beams of radiation that can be detected by telescopes on Earth, and some of them spin incredibly fast.
The first exoplanet, a planet orbiting a star other than the sun, was discovered in 1995. The exoplanet, known as 51 Pegasi b, was found by Swiss astronomers using the radial velocity method. Since then, thousands of exoplanets have been discovered, and many of them are in the habitable zones of their stars, where conditions might be suitable for life as we know it.
If you could travel at the speed of light, you could circumnavigate the Earth 7.5 times in just one second. The speed of light is about 299,792 kilometers per second, and it’s the fastest speed that anything can travel in the universe. However, according to Einstein’s theory of relativity, nothing can travel faster than the speed of light.
The light we see from the stars and galaxies in the night sky is actually millions of years old, since it takes that long for the light to travel through space and reach our eyes. This means that we’re seeing the stars and galaxies as they were millions of years ago, and they might not look the same now.
The largest asteroid in our solar system is Ceres, which is also classified as a dwarf planet. Ceres is about 590 miles (940 kilometers) in diameter, and it’s located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It was discovered in 1801 by Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi.
The most common type of star in the Milky Way is a red dwarf, which can live for trillions of years. Red dwarfs are smaller and cooler than the sun, and they’re much more common. Some estimates suggest that up to 70% of all stars in the Milky Way are red dwarfs.
The first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes was Galileo Galilei in 1609. He used it to study the moon, planets, and stars, and he made many important discoveries, including the four largest moons of Jupiter and the phases of Venus. His work helped to revolutionize our understanding of the universe and laid the foundations for modern astronomy.
The most massive black hole ever detected is known as TON 618, and it’s located about 10.37 billion light-years away from Earth. This supermassive black hole has a mass estimated to be around 66 billion times that of the sun, making it one of the most massive objects in the universe.
The International Space Station orbits the Earth at a speed of about 17,500 miles (28,000 kilometers) per hour, which means it completes one orbit in about 90 minutes. The space station is a collaboration between several space agencies, including NASA, Roscosmos, and the European Space Agency, and it’s been continuously occupied since November 2000.
There are eight planets in our solar system, and they are, in order from the sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto used to be considered the ninth planet, but in 2006 it was reclassified as a “dwarf planet.”
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that contains an estimated 100 billion stars. It’s about 100,000 light-years in diameter and about 1,000 light-years thick. Our solar system is located about 25,000 light-years away from the center of the galaxy, in a region known as the Orion Arm.
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region on Jupiter that’s been observed for more than 300 years. It’s about twice the size of Earth and is thought to be a giant storm. The exact cause of the Great Red Spot is still not completely understood, but scientists think it might be related to the planet’s strong winds and the interactions between different layers of its atmosphere.
The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1957. It weighed about 184 pounds (83.6 kilograms) and orbited the Earth every 96 minutes. Its launch marked the beginning of the Space Age and the start of the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union.
A supernova is a powerful explosion that occurs when a star runs out of fuel and collapses. These explosions can be so bright that they can outshine entire galaxies and release more energy than our sun will over its entire lifetime. Scientists study supernovae to learn about the evolution of stars and the origins of the elements in the universe.
The Hubble Space Telescope, named after astronomer Edwin Hubble, was launched into space in 1990 and has been providing stunning images of the universe ever since. The telescope has made numerous important discoveries, including evidence for the existence of dark matter and the discovery of some of the most distant galaxies ever observed.
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the sun and the moon, casting a shadow on the moon. During a total lunar eclipse, the moon can appear red, giving it the nickname “blood moon.” Lunar eclipses are relatively common and can be observed with the naked eye, but they can also be studied in detail by astronomers.
The Oort Cloud is a hypothetical region of space that’s thought to contain billions of comets and other icy objects. It’s located at the outermost reaches of the solar system and is believed to be the source of many long-period comets that occasionally pass through the inner solar system. While we haven’t directly observed the Oort Cloud, its existence is supported by observations of comets and other objects in the outer solar system.
As technological advances continue to reveal new discoveries about our world, astronomy remains one of the most interesting and active scientific subjects. Astronomy has a huge effect on our knowledge of the world around us, from the inner workings of our own solar system to the mysteries of dark matter and black holes. We may anticipate to discover much more about the cosmos in the next years, thanks to intriguing new missions and telescopes on the horizon. Whether you’re a skilled astronomer or a casual observer, astronomy is a fascinating and endlessly gratifying endeavor.