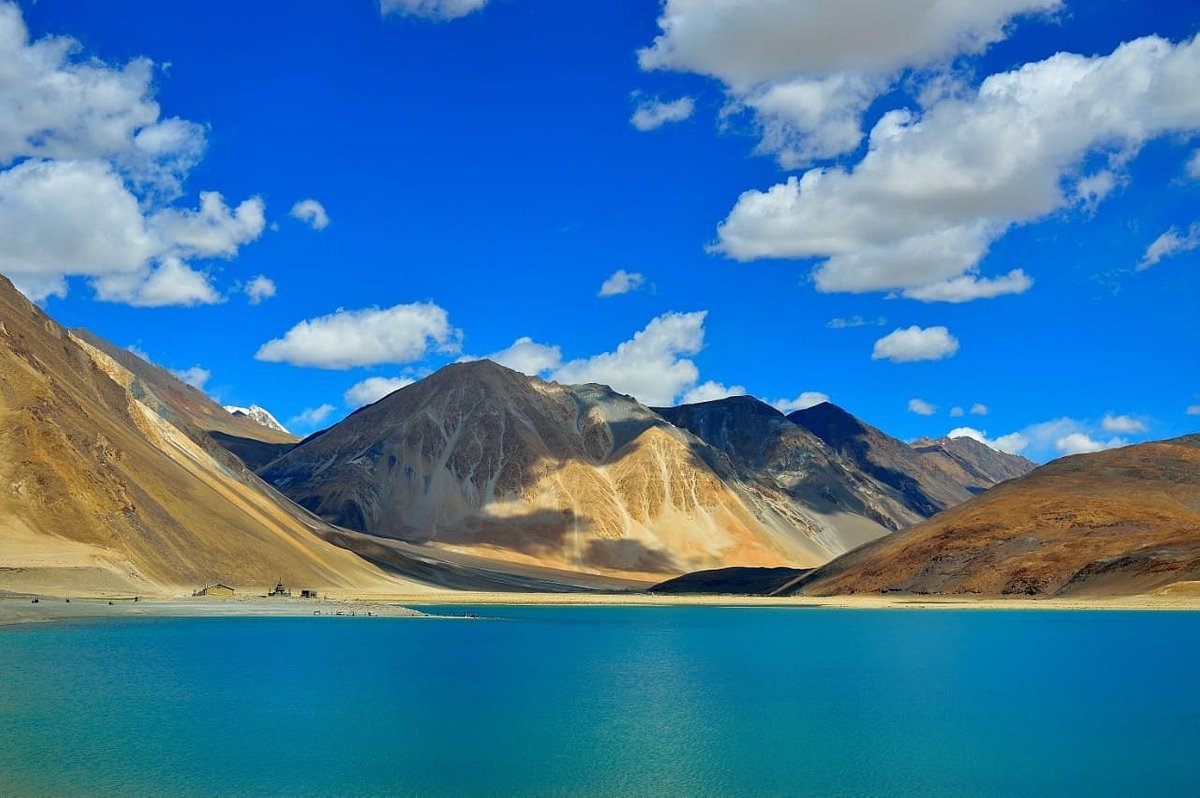
Nestled amidst the breathtaking peaks of the Himalayas, Pangong Tso emerges as a captivating jewel in the high-altitude landscapes shared by India and China. This transboundary lake, with its ethereal beauty and strategic significance, stands at an elevation that commands both awe and reverence. Beyond its natural splendor, Pangong Tso has woven itself into the tapestry of geopolitical complexities, echoing the delicate interplay between nature and human affairs. In this exploration, we unravel the mysteries of Pangong Tso through 25 historical facts and numerical trivia, delving into its cultural, environmental, and strategic dimensions. Join us on a journey to the roof of the world, where the pristine waters of Pangong Tso mirror not only the grandeur of the Himalayas but also the intricate narratives of diplomacy, conservation, and human connection.
Geographical Formation: Pangong Tso, nestled within the awe-inspiring landscapes of the Himalayas, holds the distinction of being a transboundary lake shared by India and China. Its name, Pangong, alludes to its enchanting character, portraying a sense of length and narrowness that befits its unique topography. As a high-altitude lake, it stands at an impressive elevation of approximately 4,350 meters, making it not only a breathtaking natural marvel but also one of the highest-altitude lakes globally.
Elevation: The staggering elevation of Pangong Tso at 4,350 meters (14,270 feet) above sea level contributes significantly to its allure. Situated at such heights, the lake commands unparalleled panoramic views of the surrounding Himalayan peaks, creating an ethereal atmosphere that captivates visitors. Its lofty position also bestows upon it the distinction of being among the world’s highest-altitude lakes, a testament to the grandeur of the Himalayan landscape.
Length and Width: Pangong Tso’s vast expanse covers a length of about 134 kilometers (83 miles), stretching from India into Chinese territory, with a width that fluctuates between 5 and 40 kilometers (3 to 25 miles). This impressive length and variable width contribute to the lake’s unique shape, offering a mesmerizing sight for those fortunate enough to witness its grandeur.
Dispute and Border: Beyond its natural splendor, Pangong Tso has become a focal point for geopolitical tensions between India and China. The Line of Actual Control (LAC) traverses through the lake, making it a site of contention. The ongoing border dispute has historical roots, and the region has witnessed military standoffs, underlining the complexities embedded in the Himalayan landscape.
Frozen Lake: Pangong Tso’s high-altitude location infuses it with a distinct seasonal charm. During the winter months, the lake undergoes a mesmerizing transformation as it freezes entirely, creating a vast, icy expanse. The frozen landscape not only adds to the lake’s enchantment but also presents a unique opportunity for adventurers to explore its depths on foot.
Wildlife: Pangong Tso’s pristine environment supports a variety of wildlife, making it not just a visual spectacle but also a haven for biodiversity. The lake hosts migratory bird species, creating a harmonious coexistence between the ethereal beauty of the lake and the delicate fluttering of wings. Additionally, the region around the lake is home to the kiang, a species of wild ass, and playful marmots, adding a touch of wilderness to the serene landscape.
First Western Explorer: Pangong Tso’s introduction to the Western world is credited to British explorer Thomas Montgomerie, who ventured into the region during the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India in 1856. Montgomerie’s exploration not only unveiled the lake to the world but also laid the groundwork for its recognition as a natural wonder.
Color Changing: One of Pangong Tso’s most captivating features is its ability to change colors. The lake’s hues range from various shades of blue to green, influenced by the interplay of light, weather conditions, and the lake’s depth. This dynamic palette contributes to the lake’s mystical allure, presenting different facets of its beauty depending on the time of day and weather conditions.
Freshwater Lake: Despite its high-altitude location, Pangong Tso is a saline lake, and its waters are not suitable for consumption. The lake, however, plays a crucial role in the local ecosystem, serving as a habitat for various species and contributing to the delicate balance of the surrounding environment.
High-Risk Area: Pangong Tso’s geopolitical significance and the border dispute between India and China have elevated the region to a high-risk area. Military posts from both countries surround the lake, emphasizing the strategic importance of this natural marvel in the context of broader geopolitical tensions. The heightened military presence adds an additional layer of complexity to the lake’s multifaceted identity.
Border Agreement: The Pangong Tso region has played a central role in border negotiations between India and China. The 1996 Agreement and subsequent protocols aimed to maintain peace and tranquility in the region, acknowledging the sensitivity of Pangong Tso in the context of the broader border dispute. These agreements were critical in establishing guidelines for troop movements and activities around the lake, emphasizing the importance of diplomatic solutions to maintain stability.
Tourist Attraction: Despite its challenging terrain and geopolitical complexities, Pangong Tso has evolved into a popular tourist destination, attracting adventurers and nature enthusiasts. The lake gained international fame after being featured in the Bollywood blockbuster “3 Idiots,” drawing attention to its ethereal beauty and pristine surroundings. The influx of tourists not only highlights the natural allure of the lake but also raises concerns about sustainable tourism practices in the fragile Himalayan ecosystem.
Protection Status: Pangong Tso’s ecological importance is recognized on a global scale, and the lake is part of the Ramsar Convention’s Wetland Sites. This designation underscores the need for international cooperation in preserving the lake’s unique ecosystem. However, the geopolitical context and border tensions pose challenges to joint conservation initiatives, highlighting the delicate balance between environmental protection and political complexities.
Water Volume: Pangong Tso contains a significant volume of water, although precise measurements may vary. The lake’s water volume is a critical factor in understanding its ecological dynamics and role in the local hydrology. This water reserve sustains the diverse wildlife around the lake and influences the overall health of the ecosystem.
Transboundary Conservation: The transboundary nature of Pangong Tso necessitates collaborative efforts between India and China for its conservation. However, geopolitical complexities and the ongoing border dispute create challenges in implementing joint conservation initiatives. Striking a balance between environmental stewardship and political considerations remains a crucial aspect of the region’s management.
Camping Restrictions: Pangong Tso’s sensitivity, both environmentally and geopolitically, has led to the imposition of camping restrictions. Tourists are required to obtain permits to visit the lake, and camping activities are regulated to minimize the ecological impact. These measures reflect a proactive approach to balancing the increasing tourist interest with the need to preserve the fragile ecosystem.
Nomadic Tribes: The region surrounding Pangong Tso is inhabited by the nomadic Changpa tribes. These communities have adapted their traditional lifestyles to the harsh mountainous terrain, relying on herding practices for sustenance. The coexistence of these nomadic tribes with the natural environment adds cultural richness to the region, creating a tapestry of human-nature interactions.
Military Presence: The geopolitical significance of Pangong Tso is underscored by the increased military presence in the region. Both India and China maintain military posts, adding a layer of complexity to the region’s identity. The lake’s strategic location has turned it into a symbol of national security, intertwining its natural beauty with the complexities of border defense.
Precipitation and Runoff: Pangong Tso is primarily fed by snow and glacial meltwater, highlighting the dependence of the lake on the surrounding mountainous environment. Precipitation in the form of snowfall contributes to the lake’s water levels, and the patterns of runoff impact the delicate balance of the lake’s ecosystem. Understanding these hydrological dynamics is crucial for managing the lake and its surroundings sustainably.
Diplomatic Talks: Pangong Tso has been a focal point in diplomatic talks between India and China. The region’s strategic importance and the challenges of defining the border have made negotiations complex and ongoing. Diplomatic discussions surrounding Pangong Tso reflect the broader geopolitical dynamics in the Himalayan region and underline the need for peaceful resolutions to maintain regional stability.
Pangong Lake Festival: In an effort to promote tourism and celebrate the local culture, the Ladakh administration initiated the Pangong Lake Festival. This event serves as a platform to showcase the unique cultural heritage of the region, offering visitors a glimpse into the traditions and customs of the local communities. The festival not only enhances the tourist experience but also contributes to the economic and cultural vitality of the area, creating a bridge between the global and local communities.
Bilateral Agreements: Pangong Tso’s prominence in the India-China border dispute has led to multiple bilateral agreements and negotiations. These agreements seek to manage and ease tensions around the lake, emphasizing the importance of diplomatic channels in addressing complex geopolitical issues. The ongoing discussions underline the intricacies of border management and the need for sustained dialogue between the involved nations.
Pangong Lake Development Authority: Acknowledging the delicate balance between tourism and environmental conservation, the creation of the Pangong Lake Development Authority signifies a proactive approach to sustainable development. This authority focuses on regulating activities around the lake, ensuring that tourism does not compromise the ecological integrity of Pangong Tso. Striking this balance becomes crucial in preserving the lake’s natural beauty for future generations.
Militarization Concerns: The militarization of the Pangong Tso region has raised valid concerns about its environmental impact and the potential for conflicts affecting the fragile ecosystem. Striking a balance between security concerns and ecological preservation becomes a significant challenge, highlighting the need for thoughtful and integrated strategies to mitigate the impact of military activities on the region.
Impact of Climate Change: Pangong Tso, like many high-altitude lakes, is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and glacial melt can have profound effects on the lake’s water levels and ecosystem. Understanding and addressing the implications of climate change on Pangong Tso is crucial for developing sustainable management practices and ensuring the long-term resilience of this pristine Himalayan lake.